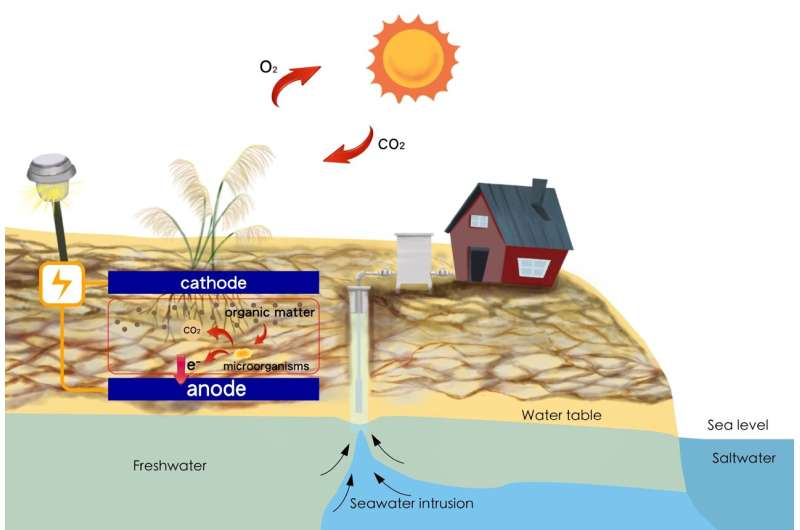
Microbial fuel cell (MFC) technology has advanced significantly in recent years, particularly in the realm of wastewater treatment. Researchers at National Taiwan University have now expanded the application of this technology to include soil, resulting in the development of soil microbial fuel cells (SMFCs) and plant microbial fuel cells (PMFCs). These innovative systems can harness organic matter from both soil and plants to generate electricity while also addressing crucial environmental issues such as greenhouse gas emissions.
The findings, published on November 3, 2025, in the Journal of Cleaner Production, highlight the dual capabilities of SMFCs and PMFCs. They not only produce electrical energy but also contribute to carbon reduction strategies, aligning with global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Exploring the Benefits of SMFCs and PMFCs
The research team focused on the effectiveness of these systems in generating power while simultaneously reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Their results indicate that both SMFCs and PMFCs can successfully produce electricity in regular soil conditions. When tested in salinized soils, the voltage generated was lower initially, but PMFCs showed a gradual increase in voltage over several months of cultivation.
In addition to power generation, the study revealed differing impacts of SMFCs and PMFCs on greenhouse gas emissions. SMFCs performed better in reducing methane emissions in normal soils, whereas PMFCs were more effective in salinized environments. This distinction showcases the adaptability of these technologies to various soil conditions.
The research also addressed the pressing issue of soil salinization, particularly in southern regions of Taiwan, where it poses a significant threat to agricultural productivity. The integration of SMFCs and PMFCs may offer a pathway to restore salinized soils, enhancing their ecological health and agricultural viability.
Future Implications and Continuing Research
The study’s lead author, Prof. Chang-Ping Yu, emphasized the potential applications of SMFCs and PMFCs in both normal and salinized soils, stating, “Overall, this study demonstrates the application potential of SMFCs and PMFCs in producing electricity and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.” The research opens avenues for further investigation into the mechanisms behind these processes and their long-term effects on soil health.
As the world seeks sustainable energy solutions and effective carbon reduction methods, the development of technologies like SMFCs and PMFCs represents a promising frontier. Continued research in this area could significantly impact agricultural practices and environmental management strategies, promoting a greener future.
For further details, refer to the publication by Chung-Yu Guan et al, titled “Greenhouse gas emission and functional gene dynamics in plant microbial fuel cells with natural and salt-affected soils,” available in the Journal of Cleaner Production.