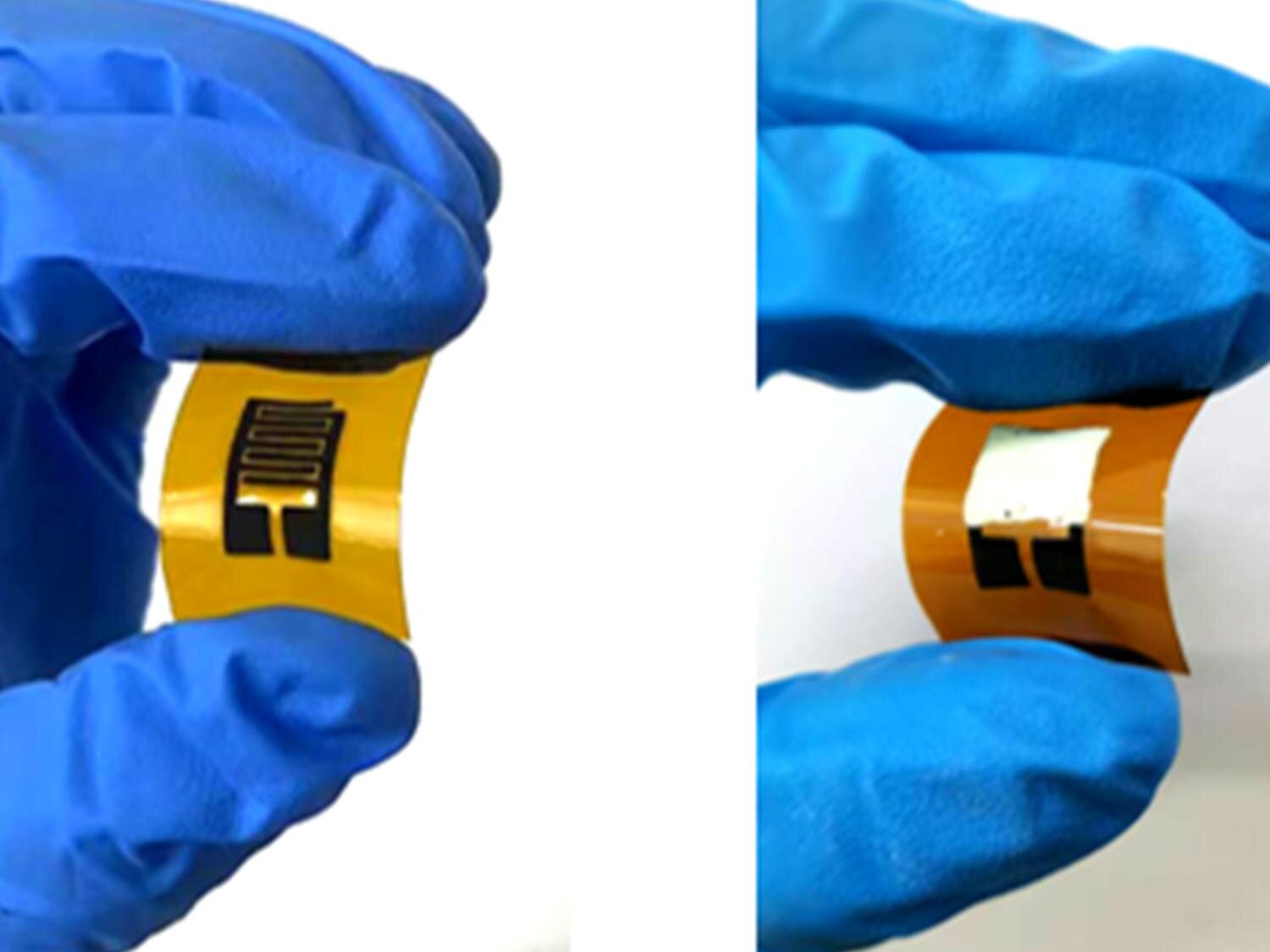
A groundbreaking study from researchers at the University of California, San Diego has unveiled a new breath sensor capable of diagnosing diabetes within minutes. This innovative technology offers a non-invasive alternative to traditional blood tests, potentially transforming diabetes screening and management.
The sensor operates by analyzing specific compounds in a person’s breath. When a person has diabetes, their breath contains elevated levels of certain volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The research team utilized advanced nanomaterials to enhance the sensor’s sensitivity, allowing it to detect these compounds quickly and accurately.
Implications for Diabetes Screening
The implications of this technology are significant. According to the International Diabetes Federation, diabetes affects more than 537 million adults globally, and early diagnosis is crucial for effective management. Traditional methods often involve blood draws, which can be uncomfortable and may deter individuals from seeking necessary testing.
This new breath sensor could lead to increased screening rates, as it is easier to use and provides results in a matter of minutes. The researchers anticipate that this technology could be particularly beneficial in remote or underserved areas, where access to healthcare facilities is limited.
Dr. Gordon W. Hwang, the lead researcher on the project, emphasized the potential of this technology to change lives. “Our goal was to create a simple, fast, and non-invasive method for diabetes diagnosis. This sensor could empower patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions quickly,” he stated.
Next Steps for Development
While the initial results are promising, further studies are needed to validate the sensor’s effectiveness across diverse populations. Researchers aim to conduct larger clinical trials to ensure accuracy and reliability. Funding for these trials is being sought from various health organizations and government grants.
The study was published in ScienceDirect, and further details can be found through credible outlets such as Medical Xpress. The research team is hopeful that with continued support, this breath sensor will soon be available for widespread clinical use.
This advancement represents a significant step forward in the fight against diabetes, illustrating how innovative technology can enhance healthcare accessibility and improve patient outcomes. As the world continues to grapple with increasing diabetes prevalence, solutions like this breath sensor may prove vital in addressing the challenge effectively.