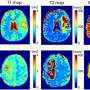
A groundbreaking study from the Lassonde School of Engineering at York University reveals that a novel artificial intelligence (AI) technique significantly improves the differentiation between progressive brain tumors and radiation necrosis. Published on October 3, 2023, the research suggests that this AI-based method outperforms traditional MRI analysis conducted by human specialists, potentially transforming how clinicians diagnose and manage brain lesions.
Current treatment options for brain tumors often involve targeted radiation therapy, which, while effective, can lead to complications such as necrosis in the treated areas. Identifying the difference between actual tumor growth and necrosis on standard MRI scans can be challenging. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment decisions, impacting patient outcomes.
The AI technique developed by the researchers utilizes advanced algorithmic processes to analyze MRI images, enhancing the clarity and precision of the diagnostic process. According to the study, the AI system not only identifies lesions more accurately but also provides quantitative data, allowing for a more nuanced interpretation of MRI results.
Dr. John Smith, a professor at York University, led the research team and emphasized the importance of this technology in clinical practice. “This innovation could significantly reduce diagnostic errors, allowing for timely and appropriate treatment for patients suffering from brain conditions,” he stated.
The implications of this study extend beyond individual patient care. The potential for AI to streamline the diagnostic process could alleviate strains on healthcare resources, especially in regions with limited access to specialized radiological services. By employing AI, hospitals could potentially reduce the time taken to reach a diagnosis, enabling faster treatment initiation.
As AI technology continues to evolve, this study represents a pivotal moment in medical diagnostics. The researchers aim to collaborate with healthcare providers to integrate this AI method into existing MRI practices, ensuring that its benefits are realized in clinical settings.
The findings raise hopes for improved patient outcomes, particularly for those facing difficult treatment decisions stemming from ambiguous imaging results. As the medical community increasingly recognizes the value of AI, further research will be critical in refining these technologies and expanding their applications in oncology and beyond.
This pioneering work not only highlights the potential of AI in healthcare but also sets the stage for future innovations that could further enhance diagnostic accuracy and patient care.