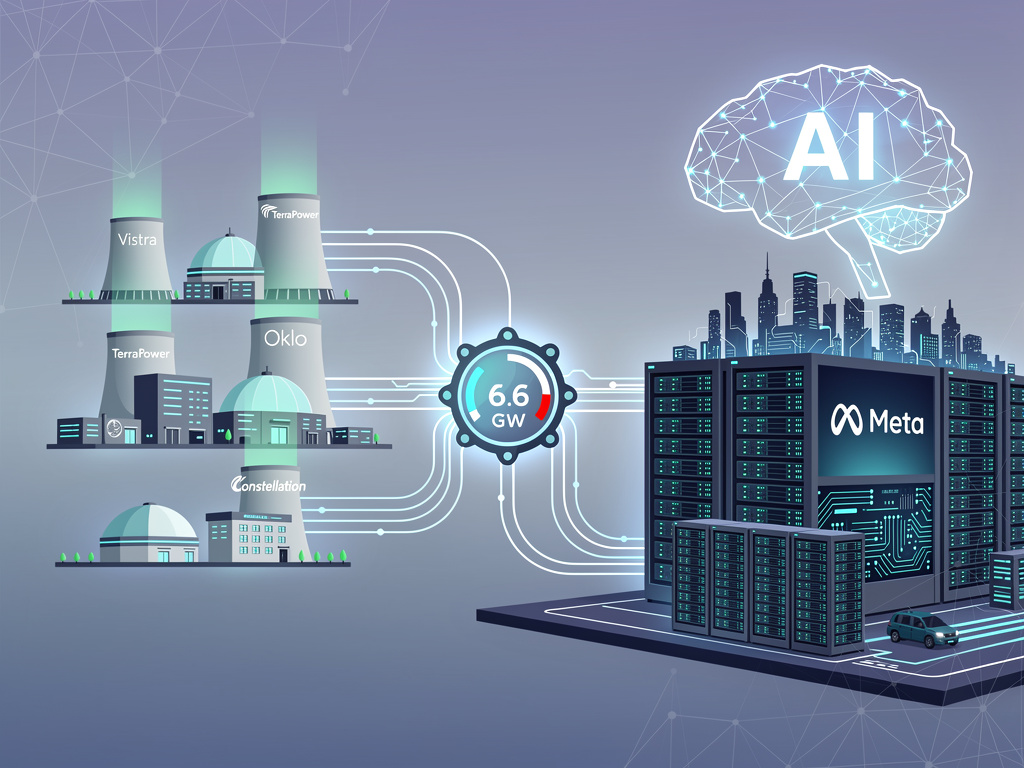
Meta Platforms Inc. announced a groundbreaking energy procurement strategy on January 9, 2026, aimed at securing up to 6.6 gigawatts of nuclear power. This historic move positions the company as a key player in the revival of U.S. nuclear energy, crucial for supporting its expanding artificial intelligence (AI) infrastructure. The agreements involve partnerships with Vistra Corp., TerraPower LLC, Oklo Inc., and Constellation Energy Corp., and are designed to address the increasing electricity demands driven by AI technologies.
The agreements include long-term power purchase contracts with three existing Vistra nuclear plants located in Illinois, Pennsylvania, and Texas. Additionally, Meta will support the development of advanced small modular reactors (SMRs) from TerraPower and Oklo. Meta describes these pacts as “landmark agreements” that not only aim to enhance nuclear technology and expand plant operations but also promise to create jobs within local American communities.
The soaring energy demands of AI have led to a significant increase in power requirements for major tech companies. Meta’s upcoming Prometheus AI supercluster, which is designed to handle extensive model scales, requires a consistent and carbon-free power supply that traditional renewable sources cannot fully provide. Industry analysts project that U.S. data centers could account for up to 8% of the national electricity consumption by 2030. This strategy represents a shift for Meta, which previously focused on renewable energy, now leaning towards nuclear for its density and reliability.
Details of the Nuclear Agreements
Under the agreements with Vistra, Meta has committed to 20-year power purchase agreements. These contracts extend the operational lifespans of Vistra’s facilities while also engaging Constellation Energy in capacity expansions. Meta’s executive, Joel Kaplan, emphasized the company’s role in becoming “one of the most significant corporate purchasers of nuclear energy in American history.” The involvement of TerraPower, backed by Bill Gates, and Oklo, supported by Sam Altman, highlights a commitment to next-generation reactor technology, which promises faster deployment and reduced costs.
The financial implications of these agreements are substantial. Following the announcement, Vistra’s shares surged by as much as 16%, reflecting investor enthusiasm for the renewed focus on nuclear power. The potential to power a city of five million households underscores the scale of Meta’s ambitions.
Joel Kaplan also noted on social media that these agreements align with national energy priorities, contributing to “clean power” and reinforcing the U.S. energy infrastructure. This move illustrates a broader trend among technology firms seeking to reduce reliance on natural gas, with nuclear energy providing a stable alternative less affected by weather conditions.
Technological Advancements and Market Impact
The Natrium reactor from TerraPower utilizes liquid sodium coolant, enhancing safety and efficiency with a targeted output of 345 megawatts per unit, and the potential for integrated energy storage. Oklo’s Aurora microreactors, ranging from 15 to 75 megawatts, are designed for quick deployment near data centers. By engaging with these innovative technologies, Meta aims to mitigate the regulatory and financial challenges that have historically impeded nuclear energy development.
As demand for uranium fuel tightens, with prices doubling since 2023, Meta’s scale could play a stabilizing role in the market. This shift comes at a time when regulatory support for nuclear energy is strengthening, aided by the Trump administration’s pro-nuclear policies.
The anticipated benefits extend beyond energy production. With thousands of high-wage jobs expected in construction, operations, and supply chains, the agreements promise significant economic impact. Local communities could see substantial tax revenues and infrastructure improvements, while concerns over safety have diminished with advancements in reactor technology.
Meta’s nuclear strategy could facilitate a major transformation in the energy landscape, potentially offsetting 20 million tons of CO2 emissions annually by 2035 compared to gas alternatives. This transition represents a significant increase in the share of clean energy provided by nuclear sources, which currently stands at 19% of the U.S. energy mix.
In conclusion, Meta’s ambitious energy strategy not only enhances its operational capabilities in the AI sector but also contributes to a broader movement towards sustainable and reliable energy sources. The company’s initiatives could redefine corporate energy strategies globally, potentially influencing how major technology firms approach their energy needs in the future.