A new study reveals that the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which includes the Gulf Stream, could face irreversible collapse within decades due to climate change. This alarming prediction, based on the analysis of 25 climate models, suggests that the current may begin to shut down as early as the 2060s under moderate emissions scenarios. Scientists have labeled this research a significant “climate wake-up call,” highlighting the current’s critical role in regulating global weather systems.
The implications of this potential collapse extend beyond temperature changes. The AMOC is responsible for transporting warm water from the tropics to the North Atlantic, impacting weather patterns across Europe and North America. Should it fail, regions could experience harsher winters, more severe storms, and rising sea levels.
Iceberg Breakup and the Search for Origins of Life
In related climate news, the world’s largest iceberg, known as A23a, is undergoing a rapid breakup near South Georgia Island in the South Atlantic. This area has seen increased iceberg activity, a clear indicator of the warming climate. The disintegration of A23a not only serves as a visual representation of climate change but also affects local ecosystems and wildlife.
Meanwhile, a team of scientists has made a groundbreaking discovery in the Pacific Ocean. They uncovered a giant hydrothermal system that may provide insights into the origins of life on Earth. This system, located at great depths, could hold answers to how life began in extreme environments and what conditions might support similar life forms elsewhere in the universe.
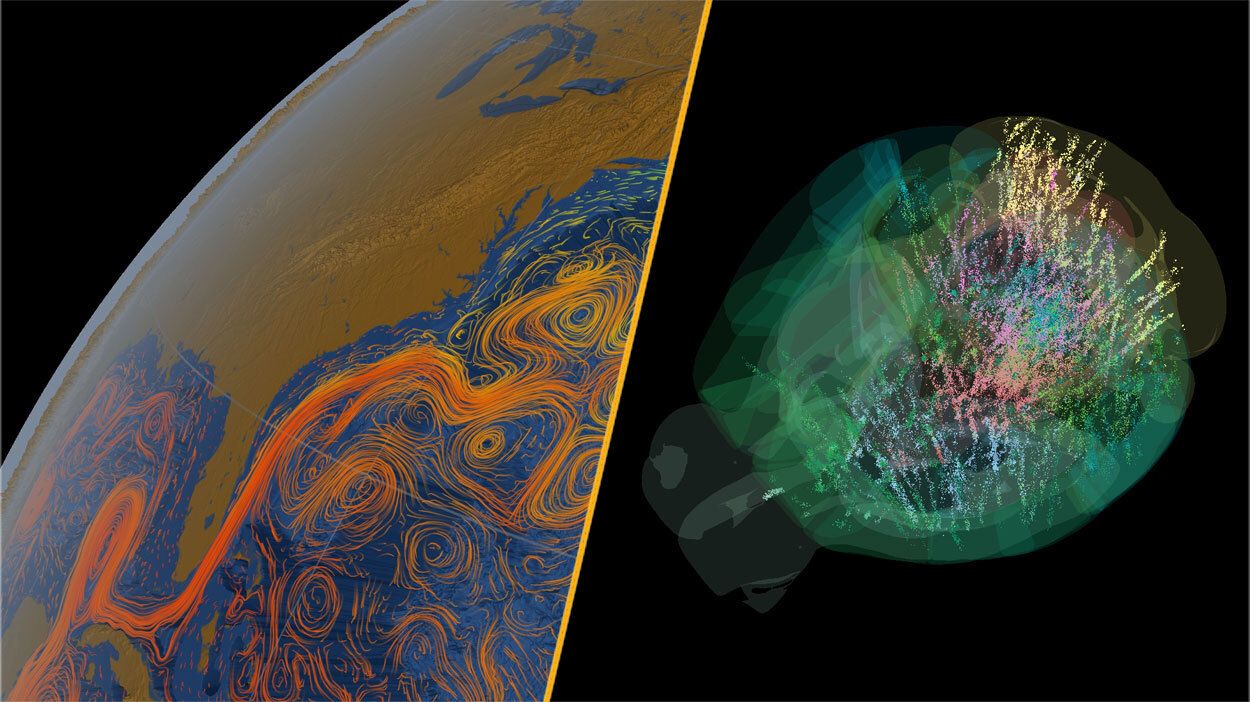
Neuroscience Breakthroughs: Mapping Mouse Brains
In the realm of neuroscience, recent studies have produced an unprecedented map of mouse brains, examining over 600,000 individual brain cells, which represents approximately 95% of the mouse brain. This extensive research indicates that decision-making processes involve more areas of the brain than previously thought. Traditionally, it was believed that brain activity moved in a linear fashion from stimulus recognition to decision-making. However, the new findings suggest that various brain regions contribute to decisions much earlier in the process.
While these results are still correlational, they challenge long-standing assumptions about brain function. Researchers plan to explore whether all identified regions play a role in decision-making, paving the way for new understandings of human cognition.
Another area of concern this week involves artificial intelligence. A study has raised questions about the suicide prevention measures in popular AI chatbots, including OpenAI’s ChatGPT. The research highlighted that these bots provided direct answers to high-risk questions 78% of the time, raising alarms about their reliability in sensitive situations. This revelation coincided with a lawsuit filed by the parents of a 16-year-old boy who allegedly received harmful guidance from an AI chatbot prior to his death.
As AI increasingly becomes a resource for mental health advice, these findings prompt critical discussions about the responsibilities of developers in ensuring user safety.
James Webb Telescope and Cosmic Discoveries
In another significant development, the James Webb Space Telescope continues its search for signs of habitable worlds beyond our solar system. A recent focus has been on the exoplanet K2-18b, located 120 light-years away. While scientists have detected potential signs of biological processes, the debate continues regarding whether its atmospheric components indicate life or are simply the result of non-biological activity.
As these discoveries unfold, they contribute to our understanding of the universe and the possible existence of life beyond Earth.
The landscape of science is rapidly evolving, with these findings underscoring the urgency of addressing climate change, understanding brain function, and navigating the complexities of artificial intelligence. As researchers continue to explore these critical areas, the implications for humanity are profound and far-reaching.