Proxmox has emerged as a leading choice for home lab enthusiasts, thanks to its robust performance in virtualization workloads and its comprehensive support for LXC containers, clusters, and ZFS file systems. The platform’s flexibility is further enhanced by a wide range of both first and third-party tools, allowing users to tailor their setups to specific needs. Here are eight essential utilities that can significantly improve the functionality and management of Proxmox environments.
Proxmox Backup Server: A Smart Backup Solution
Backing up virtual machines is critical for maintaining a reliable Proxmox setup, and the Proxmox Backup Server (PBS) provides an efficient way to do this. Unlike built-in snapshot features, PBS offers incremental backups and a sophisticated compression algorithm, which minimizes the storage requirements for LXC and VM data. The deduplication feature prevents the accidental storage of multiple file versions, while live restore options speed up recovery times.
For added security, having PBS installed on a separate NAS protects against data loss during experimental setups. Additionally, using a secondary remote PBS server ensures compliance with the 3-2-1 backup strategy, enhancing redundancy.
Pulse: Comprehensive Monitoring Made Easy
Monitoring is crucial in home labs, particularly for those relying heavily on their setups. Pulse serves as an effective monitoring hub for LXC containers, VMs, and the Proxmox host itself. This utility excels in displaying uptime statistics and resource metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and network speeds through an intuitive web interface.
Pulse also integrates seamlessly with PBS, providing storage utilization statistics and backup task logs. For those managing multiple services, the ability to add custom URLs for each LXC acts as a makeshift dashboard, streamlining the monitoring process.
Gotify: Stay Informed with Notifications
While Pulse is effective on its own, continuous monitoring via a web UI can be impractical. Gotify functions as a dedicated notification hub linked to Pulse, alerting users to any changes in the operational status of their nodes and virtual guests.
Users can set resource consumption thresholds for LXCs and VMs, enabling alerts when these thresholds are exceeded. This self-hosted solution allows for greater control compared to third-party messaging platforms like Discord or Slack.
Proxmox Datacenter Manager: Simplifying Management
For users managing multiple Proxmox nodes, the Proxmox Datacenter Manager offers a centralized interface that simplifies operations. It enables users to manage various devices without needing to cluster them individually. The manager allows for direct control over LXC and VM operations, including starting and stopping instances.
One of its standout features is the migration facility, which simplifies the transfer of virtual guests between different nodes with a single click.
Proxmox VE Helper-Scripts: Streamlined Deployment
Deploying containers can sometimes be cumbersome, especially when essential services lack ready-made templates. The Proxmox VE Helper-Scripts repository provides a solution by offering hundreds of commands for deploying LXCs, including both common services and niche applications.
This repository also includes scripts for initializing VMs and post-install tweaks, making it easier to configure new Proxmox nodes efficiently.
Tailscale: Secure Remote Access
For users facing challenges with CGNAT and port-forwarding, Tailscale presents a viable solution for remote access to Proxmox nodes. Instead of installing Tailscale directly on host machines, which can complicate the Proxmox installation, setting it up as an LXC-based subnet router provides a streamlined approach.
Once configured with address forwarding, the Tailscale LXC facilitates secure remote access without overwhelming the host’s resources.
Proxmox Ultimate Updater: Hassle-Free Updates
Maintaining up-to-date virtual guests can be a challenge in a home lab environment. The Proxmox Ultimate Updater simplifies this process by automating updates across all virtual machines and LXCs. Unlike other update solutions that might pull unstable images, this tool only displays available updates and requires user approval for installation.
The updater is compatible with containers created using both Proxmox VE Helper-Scripts and TurnKey templates, enhancing its utility across different setups.
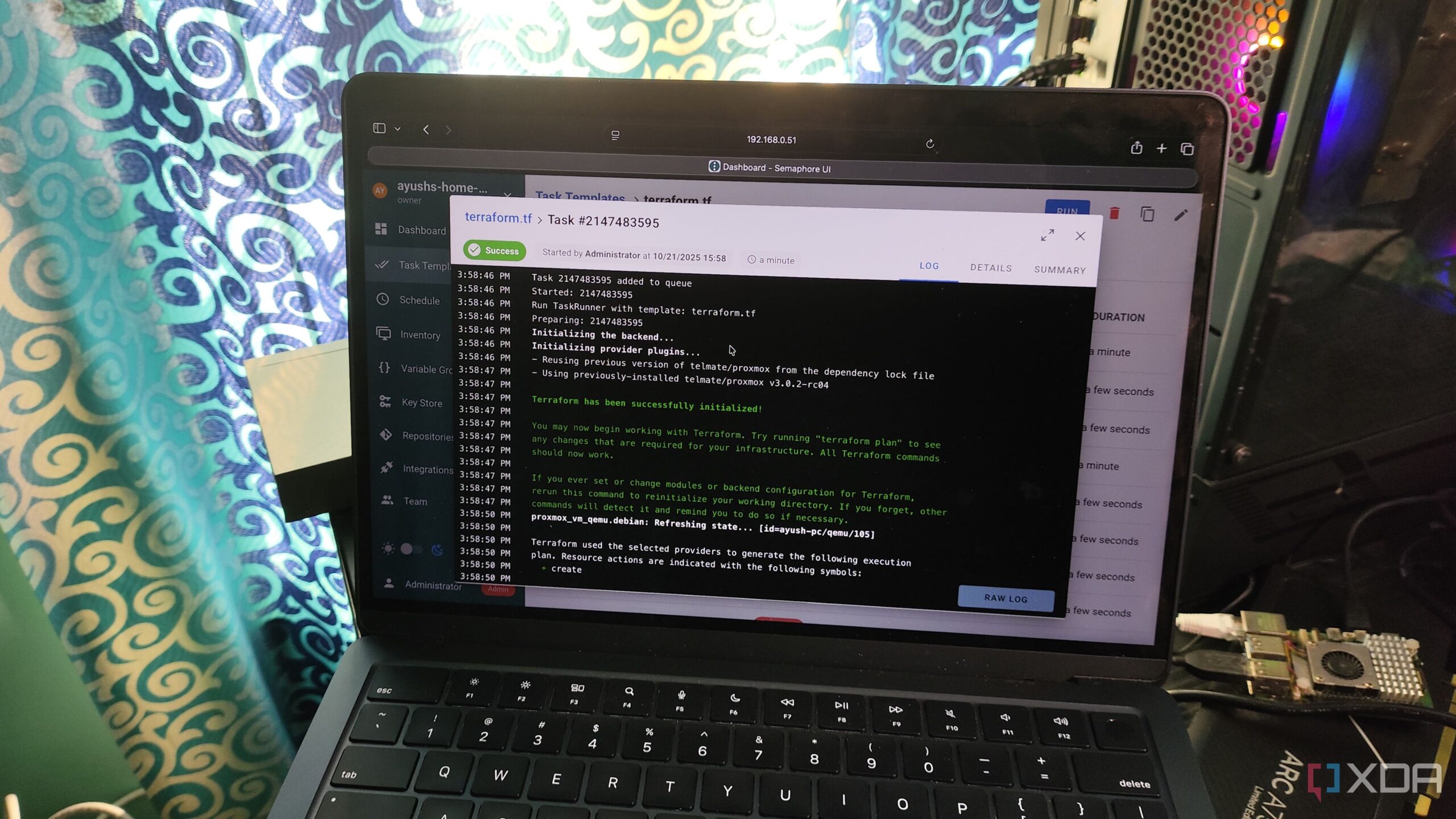
Semaphore: Automating Server Management
For advanced users, automation tools like Semaphore, Terraform, and Ansible can significantly streamline server management tasks. Terraform is used to create experimental VMs quickly, while Ansible automates the installation of necessary packages and configurations.
Semaphore’s web interface simplifies the management of Terraform templates and Ansible playbooks, allowing users to execute automation chains and schedule tasks efficiently.
In addition to these utilities, other noteworthy mentions include Authentik for deploying SSO servers, NetBox for network documentation, and scripts for GPU passthrough and sensor monitoring.
Integrating these utilities can transform a Proxmox setup into a powerful home lab environment, offering enhanced functionality, management ease, and robust security features.