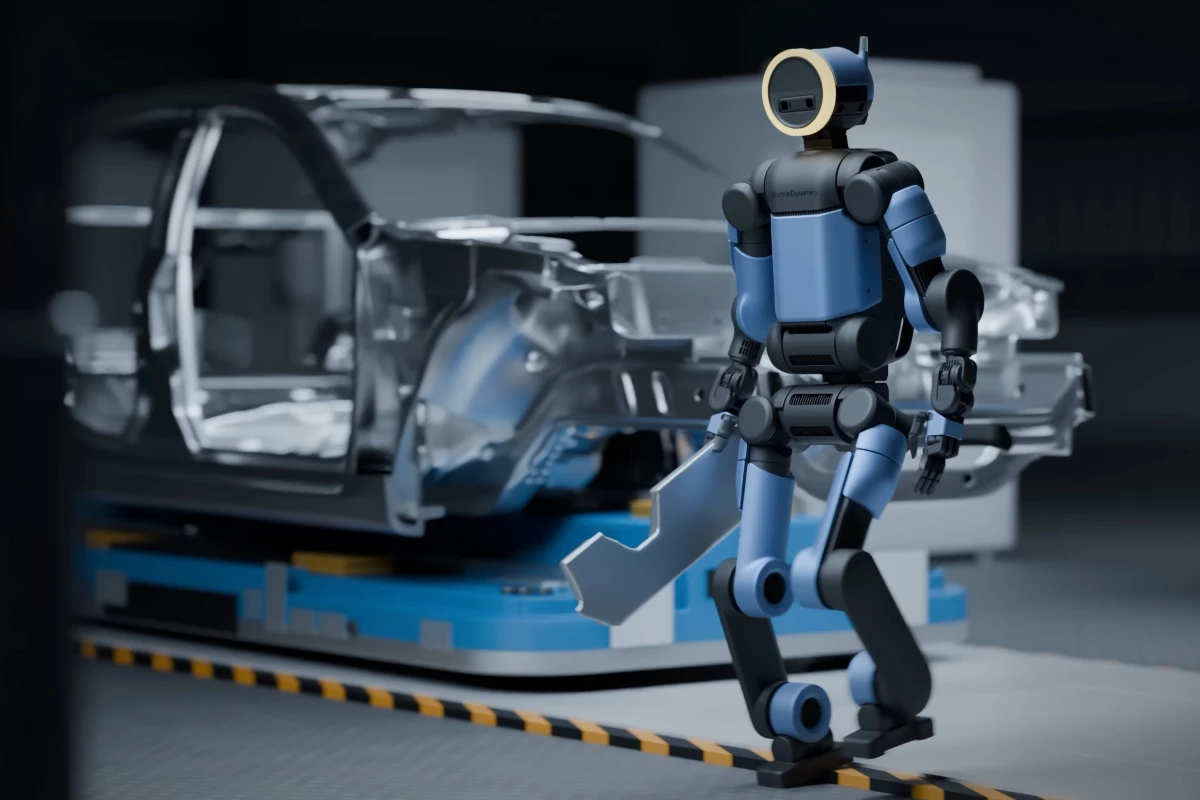
Boston Dynamics has introduced the latest version of its humanoid robot, Atlas, designed specifically for industrial applications in warehouses and factories. Production has commenced, with the first units set to begin operations at Hyundai facilities later this year. This marks a significant step in the integration of advanced robotics into everyday industrial processes.
The new Atlas stands at a height of 6.2 ft (1.9 m) and boasts 56 degrees of rotational freedom across its joints. This impressive articulation allows the robot to perform tasks requiring dexterity, such as grasping objects with independent finger movement and navigating complex environments. With a reach of 7.5 ft (2.3 m), Atlas is well-suited to the often cramped spaces found in manufacturing and warehouse settings.
Designed to operate continuously in challenging conditions, Atlas can function in temperatures ranging from -4 °F to 104 °F (-20 °C to 40 °C) and is capable of lifting loads of up to 66 lb (30 kg), with bursts up to 110 lb (55 kg). Its battery life supports four hours of operation, and it can autonomously change its power source in under three minutes, minimizing downtime.
Atlas operates in three modes: fully autonomous, human-operated via teleoperation, or through a tablet interface. Powered by advanced artificial intelligence, the robot is not only capable of executing complex movements but also of understanding and adapting to its environment. This adaptability will enable Atlas to collect valuable operational data to help optimize industrial workflows.
Boston Dynamics has partnered with DeepMind, the AI research lab affiliated with Alphabet, to enhance Atlas’s capabilities further. This collaboration aims to accelerate the learning process for the robot, allowing it to acquire new skills quickly and apply them across its fleet. Such advancements could significantly improve efficiency in various tasks, including component sequencing, machine tending, and order fulfillment.
Initial production is taking place at Boston Dynamics’ headquarters in Boston, with operational deployments scheduled for 2026 at facilities owned by Google DeepMind and Hyundai. The partnership with Hyundai is particularly noteworthy, as the automotive giant is a majority shareholder in Boston Dynamics and plans to establish a new robotics facility capable of producing 30,000 robots annually. This facility may also manufacture other models, such as the Spot robot.
Zack Jackowski, General Manager of Atlas at Boston Dynamics, emphasized the robot’s design efficiency, stating, “Our new Atlas is the most production-friendly robot we’ve ever designed.” He noted that the latest iteration of Atlas features fewer unique parts, enhancing compatibility with automotive supply chains. This integration is expected to improve both reliability and the economic viability of robotic solutions in industry.
The launch of Atlas signals a competitive shift in the robotics landscape, as it follows recent developments in China where UBtech unveiled its Walker S2 humanoid robots for various industrial applications. The increasing focus on deploying humanoid robots across both American and Chinese factories indicates a growing recognition of their potential to enhance productivity and operational efficiency.
As the robotics industry evolves, Atlas represents not only a technological advancement but also a step toward a future where humanoid robots could become integral to everyday life, assisting in both industrial and domestic settings.